Tree
컴퓨터 과학에서 Tree는 계층 구조의 추상 모델이다.
즉, 상하관계가 있고 abstract data type이다.
Tree는 부모 자식 관계를 가진 노드들로 구성되어 있다.
트리 용어 정리
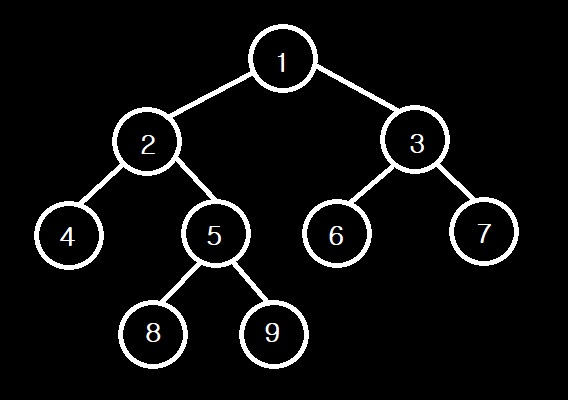
- Root
- 부모가 없는 노드
- 1번 노드가 Root 노드이다.
- Internal node(=
Non-leaf node)- 자식이 적어도 하나 있는 노드
- 1, 2, 3, 5
- non-terminal 노드라고도 한다.
- External node(=
Leaf node)- 자식이 없는 노드
- 4, 8, 9, 6, 7
- terminal 노드라고도 한다.
- Ancestor
- 한 노드를 기준으로 그 노드의 위로 연결된 노드들
- 자기 자신도 포함
- 9의 조상은 1, 2, 5이다.
- 4, 6, 7, 3은 9와 직접 연결되어 있지 않으므로 조상이 아니다.
- Descendant
- 한 노드를 기준으로 그 노드의 아래로 연결된 노드들
- 자기 자신도 포함
- 조상 노드의 역이다.
- 9는 1, 2, 5의 후손이다.
- SubTree
- 한 노드를 기준으로 그 노드의 모든 후손으로 구성된 트리
- 2 - 4 - 5 - 8 - 9 tree는 전체 트리의 Subtree이다.
- Edge
- 관계가 있는 두 노드간에 연결선
- 1 - 2 / 5 - 9 etc..
Path- 어떤 노드에서 다른 노드로 가는 방법 / 경로
- Sibling
- 같은 부모를 가진 노드들의 집합
- 4 - 5는 Sibling이다.
- 2 - 3은 Sibling이다.
- etc..
Depth- Root node까지의 edge의 수
- 5의 depth는 2이다.
Level- Root node까지의 node의 수
- 흔히 depth + 1이다.
- 5의 level은 3이다.
- level 3: 4, 5, 6, 7
Height- Leaf node까지의 edge의 수
- 5의 height는 1이다.
- 4의 height는 0이다.
Tree Interface Method
class Node{
E element
Node* parent;
List<Node*> children;
Node parent(); //현재 노드의 부모노드를 반환한다.
list<Node> children(); //현재 노드의 자식들을 반환한다.
bool isRoot(); //root노드인지 check
bool isLeaf(); //leaf노드인지 check
}
class Tree{
Node* root;
List<Node*> nodes;
int size(); //tree의 사이즈 반환
bool empty(); //tree가 비어있는지 check
Node root(); //root 노드를 반환한다.
list<Node> nodes(); //전체 트리를 반환한다.
}일단 참고
depth 함수 recursion 함수로 구현
int depth(v){
if(v.isRoot())
return 0;
else
return 1+depth(v.parent())
}Height 함수 구현
int height(v){
if (v.isLeaf())
return 0;
else{
for(auto temp : v.children())
h = max(h, height(u))
return h + 1;
}
}Time Cost: O(# of descendants)
Space Cost: O(h of descendents)
Traversal
Preorder Traversal
- 1 - 2 - 4 - 5 - 8 - 9 - 3 - 6 - 7
- Example: 프린터
- Algorithm
Algorithm preOrder(v) visit(v) //여기가 keypoint for each child w of v preorder (w)
Postorder Traversal
- 4 - 8 - 9 - 5 - 2 - 6 - 7 - 3 - 1
- Example: 저장된 폴더 사이즈 계산
- Algorithm
Algorithm postOrder(v) for each child w of v postOrder (w) visit(v) //여기가 keypoint
Inorder Traversal
- 4 - 2 - 8 - 5 - 9 - 1 - 6 - 3 - 7
- Example: binary tree 그리기
- Algorithm
Algorithm inOrder(v) if v.isLeaf() inOrder(v.left()) visit(v) //여기가 keypoint if v.isLeaf() inOrder(v.right())
Euler-Tour Traversal
1 - 2 - 4 - 2 - 5 - 8 - 5 - 9 - 5 - 2 - 1 - 3 - 6 - 3 - 7 - 3 - 1
자기 자신을 다시 돌아옴
preoreder/ inoreder/ postoreder의 종합 형태
Example: Print Arithmetic Expressions
Algorithm printExpression(v) if(!v.isExternal()){ print("("); //preorder printExpression(v.left()); } print(v.element()) //inorder if(!v.isExternal()){ printExpression(v.right()) print (")") //postorder }Algorithm
Algorithm EulerTour(v) visit(v); //preorder EulerTour(v.Left()); visit(v); //inorder EulerTour(v.Right()); visit(v); //postorder
Level-Order Traveral
- 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9
- 각 레벨 순서에 따라 탐색 (너비 우선 탐색)
- Queue를 사용하여 구현한다.
- Algorithm
- 재귀함수가 아님을 인지하자.
Algorithm levelOrder(v) Q.enqueue(v) while (!Q.isEmpty()){ u ← Q.dequeue() visit(u) for each child w of u Q.enqueue(w) }
- 재귀함수가 아님을 인지하자.
Time Cost: O(n)Space Cost O(L)- L: i번째 노드 수 들 중 가장 큰 값 (0 ⪯ i ⪯ h)
Binary-Trees
Binary tree는 다음의 조건을 따르는 순서화된 트리이다.
- 각 non-leaf 노드는 최대 두개의 자식을 가진다.
- 한 노드의 자식은 순서화된 페어이다.
- 즉, 왼쪽 자식과 오른쪽 자식은 순서를 가진다.(상하 관계가 생긴다)
용어 정리
- 즉, 왼쪽 자식과 오른쪽 자식은 순서를 가진다.(상하 관계가 생긴다)
- Proper binary tree
- 각 노드가 2개 또는 가지지 않을 때 Proper binary tree이다.
- 위 그림은 Proper binary tree이다.
- Complete binary tree
- 모든 노드가 Left child 부터 채워졌을 경우 Complete binary tree이다.
- 위 그림은 4번 노드의 자식이 5번 보다 먼저 채워져야 하나 그렇지 않으므로, Complete binary tree가 아니다.
Binary Tree의 속성
n: 노드의 수
m: non-leaf 노드의 수
l: leaf 노드의 수
h: height
- General Binary Tree
- h+1 ⪯ n ⪯ 2^(h+1) - 1
- h ⪯ m ⪯2^h - 1
- (0 or 1) ⪯ l ⪯ 2^h
- log(n+1) - 1 ⪯ h ⪯ n - 1
- 위 식으로 유도된 big oh notation
- O(logn) ⪯ O(h) ⪯ O(n)
- Propoer Binary Tree
- l = m + 1
- logl ⪯ h ⪯ m
- n = 2l - 1
- h ⪯ (n-1)/2
- l ⪯ 2^h
- log(n+1) - 1 ⪯ h
Structure for Tree
Linked structure
General Trees
Binary Trees
자식이 최대 2개 까지만 가질 수 있으므로 children을 벡터로 구현할 필요가 없다.
Algorithm
class Node{ E element Node* parent; Node* Left_child; Node* Right_child; Node parent(); //현재 노드의 부모노드를 반환한다. Node Left_child(); Node Right_child(); bool isRoot(); // root노드인지 check bool isLeaf(); // leaf노드인지 check }
Array-Based Binary Trees
Array-based Tree는 Heap에서 다시 확인
- 일반 배열을 배열 기반으로 만들기는 불가하다.
- 자식의 수가 정해져 있지 않으므로 배열 할당이 동적이며 매우 비효율적이다.
- Array의 index로 자식을 표현한다.
- 2진 트리는 자식을 최대 2개를 가질 수 있으므로, 자식이 없어도 2칸을 비워두고 그 다음 칸에 다른 노드의 자식을 넣음으로써 표현이 가능하다.
- 각 level에 노드 수는 2^n 이므로, 각 level마다 할당 해주어야 할 배열 공간은 2^n이다.
- Algorithm
Time Cost: O(n)Node v is stored at A[index] root_index = 1 if node is the left child of parent(node) left_child_index = 2 * parent_index if node is the right child of parent(node) right_child_index = (2*parent_index) + 1
Space Cost: O(2^n) - n개의 노드가 right child로만 추가가 된다면 저장공간은 2^n로 커진다.
- max child num + 1
'DataStructure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Binary Search Tree (0) | 2021.01.20 |
|---|---|
| Heap (0) | 2021.01.20 |
| PriorityQueue(PQ) (0) | 2021.01.19 |
| Recursion (0) | 2021.01.19 |
| Queue (0) | 2021.01.19 |




최근댓글