Graph
graph is a pair(V, E)
- V: a set of nodes, called vertices
- 노드의 집합
- E: a collection of pairs of vertices, called edges
- vertices들을 잇는 연결 선의 집합
Tree is special case of graph
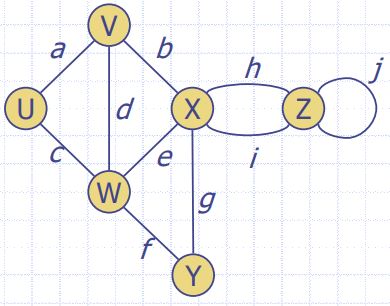
Edge의 유형
- Directed edge
- Directed graph
- Undiredted edge
- Undiredted grap
용어
- End vertices (endpoints)
- U, V are the
End verticesof the edge a - 어떤 edge에서의 양 끝 vertices
- U, V are the
- Incident edges
- a, d, b are incident on V
- 어떤 vertex에서 연결된 edges
- Adjacent vertices
- U, V are adjacent
- edge로 연결된 vertices
- Degree
- Num of incident edges
- X has degree 5
- 어떤 vertex와 연결된 edge의 수
- indegree / outdegree
- Parallel edges
- h, i are parallel edges
- 같은 vertices들을 잇는 edges
- Self-loop
- j is a self-loop
- 어떤 vertex와 자기 자신을 잇는 edge
- Path
- Sequence of vertices
- ex) P1 = (U, W, X, Y, W, V)
- Simple path
- cycle이 없는 path
- ex) P2 = (V, X, Z)
- Cycle
- 어떤 vertex에서 다시 자기 자신으로 돌아오는 path
- P3 = (W, X, Y, W)
- Simple cycle
- 시작과 끝을 제외하고는 중복되는 vertex가 없는 cycle
- P3는
simple cycle이다. - P4 = (U, W, X, Y, W, V, U) 는 W가 중복되므로 Non-simple cycle이다.
- Lenth of Path
- 경로 중에 있는 edges의 수
- len(P1) = 5
- len(P2) = 2
Attribute
n: num of vertices
m: num of edges
- Sum of all degree is 2m
- In simple graph, m ≤ n(n-1)/2
- Pf) 최대 갯수 m은 n개의 vertex들이 서로 연결된 상태일 때 최대를 가진다.
- 어떤 vertex가 가지는 degree는 (n-1)이다.
vertex가 n개이므로 총 degree는 n(n-1)이 성립한다. - 전체 degree의 합은 2m이므로, 2m = n(n-1)이 성립하고, m = n(n-1)/2 이다.
- 최대 m개 일때 m = n(n-1)/2 이므로
- m ≤ n(n-1)/2 이다.
- 어떤 vertex가 가지는 degree는 (n-1)이다.
- Pf) 최대 갯수 m은 n개의 vertex들이 서로 연결된 상태일 때 최대를 가진다.
- In directed graph, It is the same as the above.
- Property 1
- 하나의 vertex에서 나가는 edge의 수를 a라 하자.
그렇다면 다른 하나의 vertex는 들어오는 edge가 존재할 것이며, 그 vetex의 수는 a와 동일하다.
나간만큼 들어가야하기 때문이다.
outdegree의 전체 합을 S라 하면, indegree의 전체 합 또한 같으므로, S이다.
그리고 outdegree는 전체의 edge의 개수와 같으므로 m개이며, S = m이다.
따라서, 전체 degree의 합은 (Sum of outdegree + Sum of indegree) = 2S = 2m이다.
- 하나의 vertex에서 나가는 edge의 수를 a라 하자.
- Property 2
- 전체 vertex의 수를 n, 전체 edge의 수를 m이라 하자.
degree의 합이 최대일 경우를 생각해보자.
하나의 vetex에서 나가거나 들어오는 edge의 수는 자기 자신을 제외한 나머지 vertex와 연결된 edge, (n - 1)개이다.
이러한 vertex가 n개 있으므로, n(n-1)이 최대 degree의 합이다. 그리고, Property1에서 전체 degree의 합은 2m임을 구했다.
2m = n(n-1)이 성립한다. 하지만 n(n-1)이 최대 degree이므로, 2m <= n(n-1)이 된다.
따라서, m <= n*(n-1)/2이다.
- 전체 vertex의 수를 n, 전체 edge의 수를 m이라 하자.
- Property 1
Method of the Graph
접근 메소드
- edge 메소드
- endVertices(): edge의 두 endvertices의 리스트들을 보여준다.
- opposite(): edge로 연결된 v의 반대 vertex를 반환한다.
- vertex 메소드
- isAdjacentTo(v): 현재의 vertex와 v와의 관계가 있는지 bool로 반환한다.
갱신 메소드
- insertVertex(o)
- insertEdge(v, w, o)
- eraseVertex(v)
- eraseEdge(e=(v, w))
반복자 메소드
- neighbors(v): v와 관계있는 vertices의 리스트들을 보여준다.
- vertices(): 그래프의 모든 vertices를 보여준다.
- edges(): 그래프의 모든 edges를 보여준다.
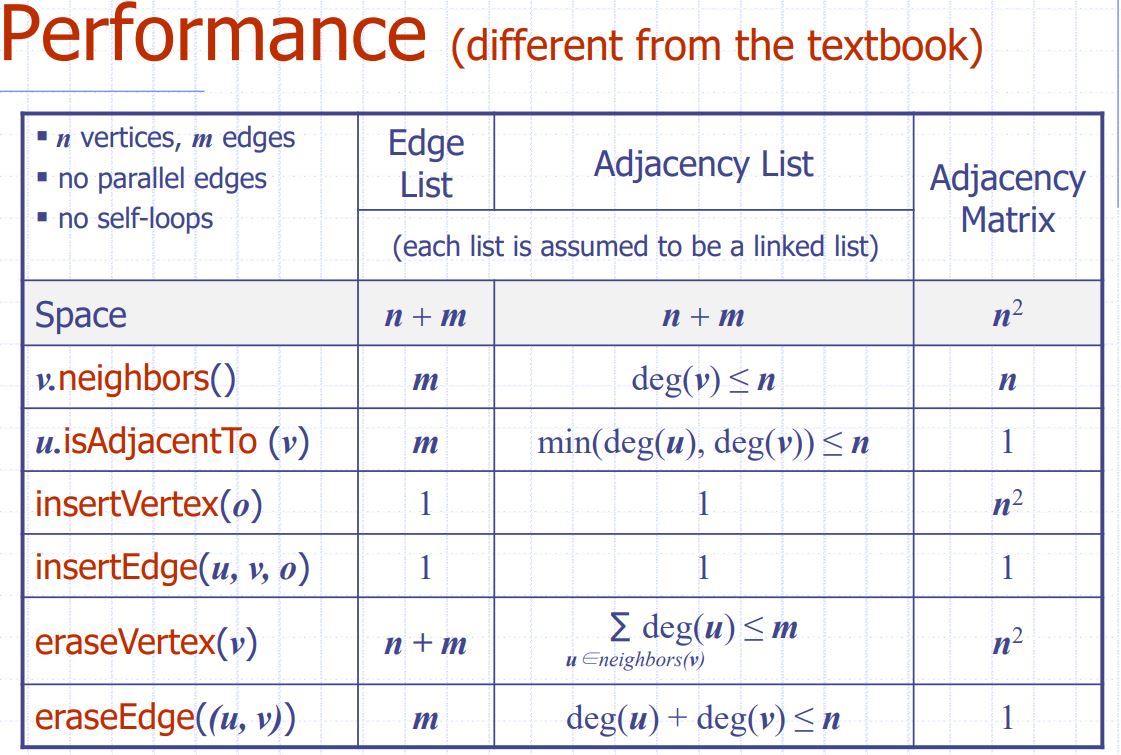
Graph Structure
3가지 있음: edge, adjacnecy, adjacency matrix
Linked List로 가정한다.
- Edge List Structure
- vertices의 리스트와 edges의 리스트를 구현하고 저장한다.
- edges 리스트에 vertices의 관계가 저장된다.
- O(n+m) Space가 필요하다.
- vertices의 리스트와 edges의 리스트를 구현하고 저장한다.
- Adjacnecy List Structure
- vertices들을 array나 hash table로 저장한다.
- edge의 관계는 저장된 bucket에서 LinkedList로 관계가 되는 vertex를 이어나간다.
- O(n+m) Space가 필요하다.
- vertex와 edge가 활발히 추가되고 삭제될 때, neighbors를 자주 가져와야 할 때 효율적이다.
- 대부분의 SNS가 이 structure이다.
- vertices들을 array나 hash table로 저장한다.
- Adjacnecy Matrix List Structure
- n * n의 2차원 배열로 저장한다.
- 행과 열에 각각 vertex를 추가한다.
- edge의 관계는 2차원 배열의 [vertex_x, vertex_y] 위치에 관계가 있음을 표시한다.
- O(n^2) Space 가 필요하다.
- 관계는 자주 바뀌나 vertex는 자주 바뀌지 않는 경우에 효율적이다.
- n * n의 2차원 배열로 저장한다.
SubGraph
subgraph: 어떤 그래프 안에 포함되는 그래프
- Spanning subgraph
- 모든 vertex를 포함하는 subgraph
- 모든 edge를 포함하지 않을 수 있다.
- Induced subgraph
- subgraph의 모든 vertex간에 edge를 모두 포함할 경우
Connectivity
A graph is connected if there is a path between every pair of vertices
모든 vertices들에 대하여 두 vertices를 선택했을 때 서로 갈 수 있는 Path가 존재 해야한다.
Connected Component
Maximal connected subgraph of G
전체 그래프에서 subgraph들 중 최대로 연결된 subgraph
Trees and Forest
Tree is undirected graph T such that
T is connected
T has no cycles (acyclic graph: cycle이 없는 graph)
=> connected acyclic graph
- root가 없는 경우: free tree
- root가 있는 경우: rooted tree
Forest is set of trees
The connected components of a forest are trees.
Spanning Tress and Forest
Graph Traversal
visit all the vertices in some specific order based on graph's topology
Two issues
- disconnected graph
- cycle
Basic process
- mark all vertices "Unvisited"
- for each v ∈ V:
if v is "Unvisited":
DFS vs BFS
| Application | DFS | BFS |
|---|---|---|
| Spanning forest | Y | Y |
| connected components | Y | Y |
| paths | Y | Y |
| cycles | Y | Y |
| Shortest paths | N | Y |
'DataStructure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Breadth-First Search(BFS) (0) | 2021.01.20 |
|---|---|
| Depth-First Search(DFS) (0) | 2021.01.20 |
| Hash Tables (0) | 2021.01.20 |
| AVL Tree (0) | 2021.01.20 |
| Maps & Dictionary (0) | 2021.01.20 |




최근댓글